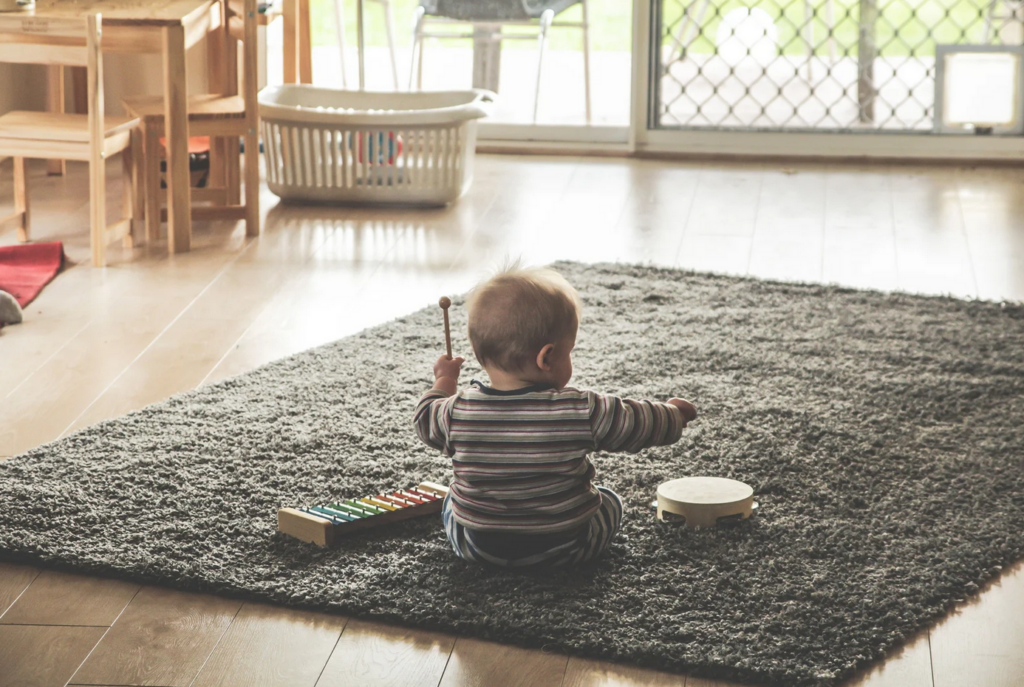
What is Music Therapy?
Music therapy is a way of using the power and beauty of music to heal. It’s been proven to help with mental, emotional, physical and cognitive concerns. Music therapy has been shown to be useful in addressing various issues that can come up with autism such as social skills, stress, language development, and more.
“Music therapy” is the use of music to achieve five specific factors:
- Attention
- Excitement
- Cognition Behaviour
- Communication
Music increases attention by providing a focus for listening; alters behaviour in that it promotes self-expression or facilitates group participation with reduced inhibitions from fear of social disapproval; regulates cognitive activity through focused concentration on an assigned task (like memorizing).
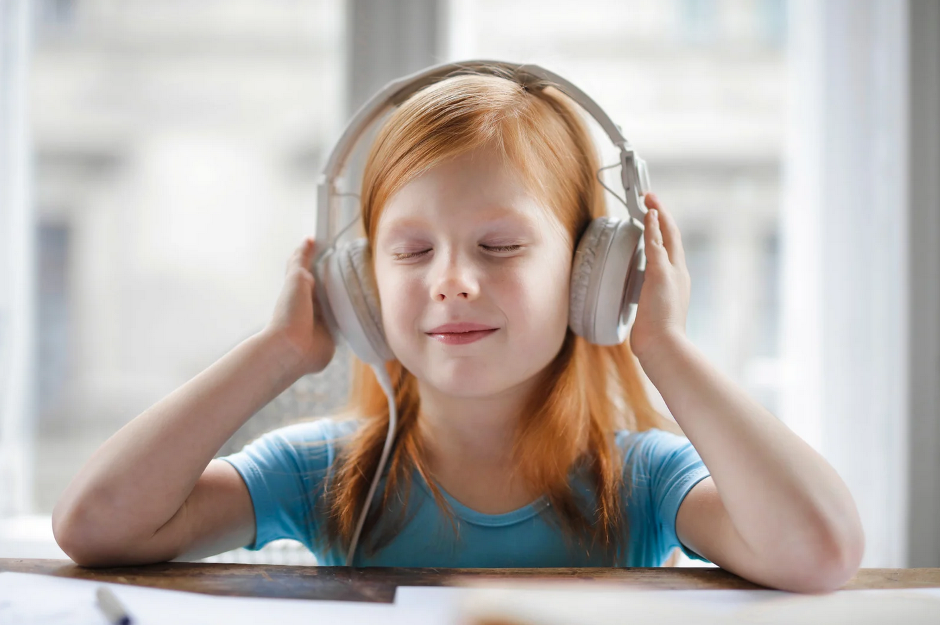

More than a quarter of autistic children are not able to talk, most commonly suffering from speech impediments that result in communication and social impairments. The ones who do have the capacity for vocalization usually sound hoarse, deepened-toned, and disconnected.
Music, songs and melodic speech can help an autistic child pay attention to others. Imitating the rhythm of words and singing will often cause more interaction with spoken signs or drawings. The reader’s attention will be drawn to it since his/her interest in language is stimulated while he/she listens to a song or hears rhythmic sounds from other people talking.

Music can strengthen the 5 factors mentioned as follows:
- Stimulation of arousal: One way to engage an autistic child is by stimulating their arousal. This can be achieved through music, as they are low-functioning and do not participate in any activities.
- Emotion adjustment: New research has indicated that limbic system problems are at the heart of autism. When autistic children have their hearing stimulated by music, it causes them to become excited and less anxious.
Note that the type of music is very important in this category. The use of inappropriate music can have a negative effect on children’s moods and stress levels.
- Cognition adjustment: There are various aspects of cognition that music can affect, and it also modulates the child’s social cognition.
- Modification of communication: The first duty of a music therapist is to establish therapeutic communication-or in other words, communicating with children and then seeing how the child relates to that music.
- Behaviour modulation: Behaviour here refers to more motor functions, like synchronizing movement with music. Activating this part of the brain can be done through means (i.e., through synchronization).
Reasons why music is useful for therapeutic purposes:
- The human nervous system and the functions of the body have a rhythmic pattern
- The body is able to coordinate itself with rhythmic factors
- Music strengthens nerve pathways
Music therapy is a powerful therapeutic tool that can help autistic children develop communication skills and improve their social interactions. There is hope for your child!